 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Advancing Wound Filling Extraction on 3D Faces: An Auto-Segmentation and Wound Face Regeneration Approach
1 Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Quy Nhon University, Quy Nhon City, 55100, Viet Nam
2 Applied Research Institute for Science and Technology, Quy Nhon University, Quy Nhon City, 55100, Viet Nam
3 CIRTECH Institute, HUTECH University, Ho Chi Minh City, 72308, Viet Nam
* Corresponding Author: H. Nguyen-Xuan. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 139(2), 2197-2214. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.043992
Received 18 July 2023; Accepted 23 October 2023; Issue published 29 January 2024
Abstract
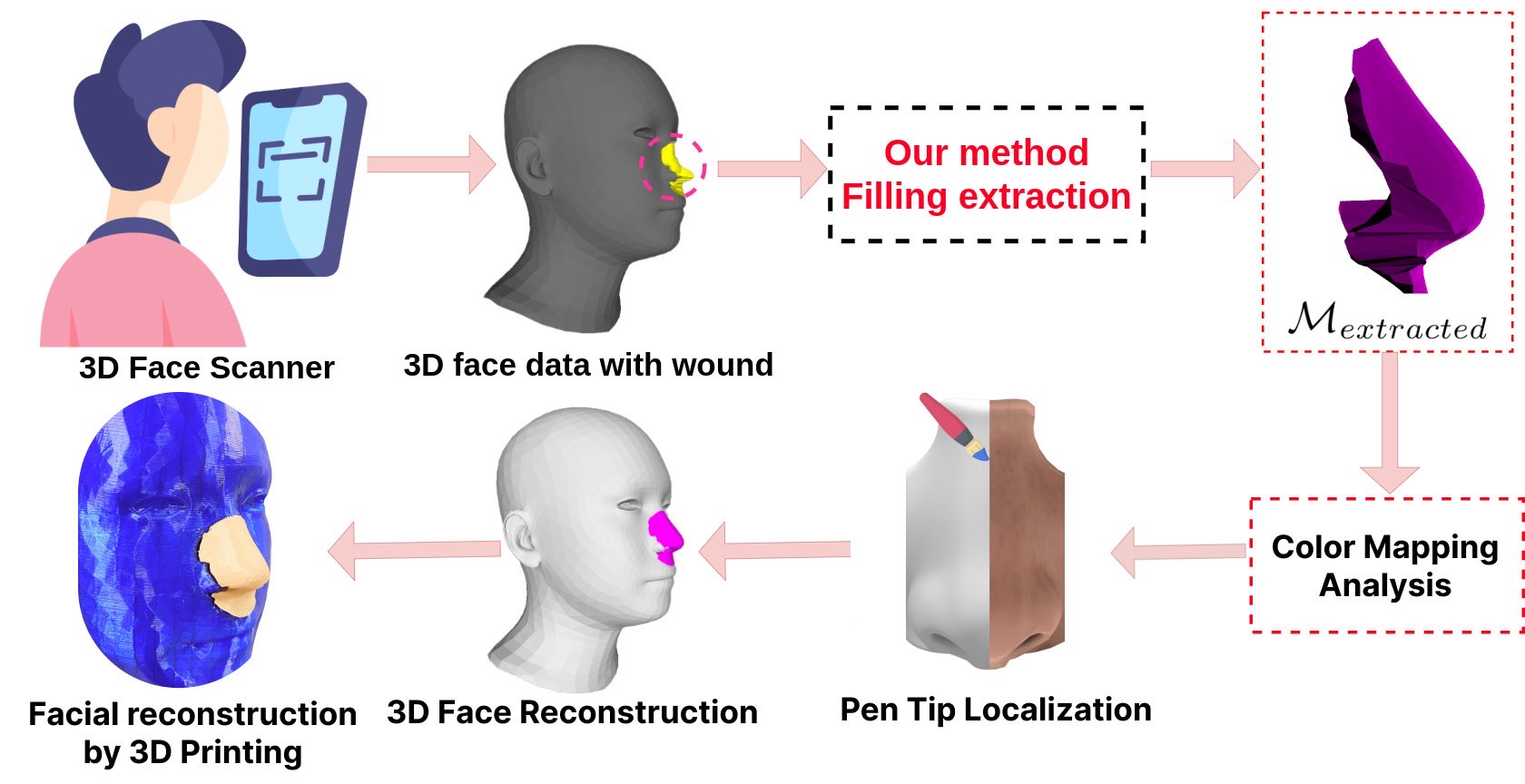
Facial wound segmentation plays a crucial role in preoperative planning and optimizing patient outcomes in various medical applications. In this paper, we propose an efficient approach for automating 3D facial wound segmentation using a two-stream graph convolutional network. Our method leverages the Cir3D-FaIR dataset and addresses the challenge of data imbalance through extensive experimentation with different loss functions. To achieve accurate segmentation, we conducted thorough experiments and selected a high-performing model from the trained models. The selected model demonstrates exceptional segmentation performance for complex 3D facial wounds. Furthermore, based on the segmentation model, we propose an improved approach for extracting 3D facial wound fillers and compare it to the results of the previous study. Our method achieved a remarkable accuracy of 0.9999993% on the test suite, surpassing the performance of the previous method. From this result, we use 3D printing technology to illustrate the shape of the wound filling. The outcomes of this study have significant implications for physicians involved in preoperative planning and intervention design. By automating facial wound segmentation and improving the accuracy of wound-filling extraction, our approach can assist in carefully assessing and optimizing interventions, leading to enhanced patient outcomes. Additionally, it contributes to advancing facial reconstruction techniques by utilizing machine learning and 3D bioprinting for printing skin tissue implants. Our source code is available at https://github.com/SIMOGroup/WoundFilling3D.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools