 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
A New Method for Diagnosis of Leukemia Utilizing a Hybrid DL-ML Approach for Binary and Multi-Class Classification on a Limited-Sized Database
1 Department of Electronics & Telecommunication, Lavale, Symbiosis Institute of Technology, Symbiosis International (Deemed University), Pune, Maharashtra, 412115, India
2 Electronics & Telecommunication, Dr. Vithalrao Vikhe Patil College of Engineering, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, 414111, India
3 Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Department, Symbiosis Institute of Technology, Symbiosis International (Deemed) University, Pune, 412115, India
4 Symbiosis Centre of Applied AI (SCAAI), Symbiosis International (Deemed) University, Pune, 412115, India
5 Centre for Advanced Modelling and Geospatial Information Systems (CAMGIS), School of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Faculty of Engineering & IT, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, Australia
6 Earth Observation Centre, Institute of Climate Change, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Bangi, Selangor, 43600, Malaysia
7 Department of Geology & Geophysics, College of Science, King Saud University, P.O. Box 2455, Riyadh, 11451, Saudi Arabia
8 Department of Science Education, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon-si, 24341, Korea
* Corresponding Authors: Shilpa Gite. Email: ; Chang-Wook Lee. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Computer Modeling of Artificial Intelligence and Medical Imaging)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 139(1), 593-631. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.030704
Received 19 April 2023; Accepted 06 September 2023; Issue published 30 December 2023
Abstract
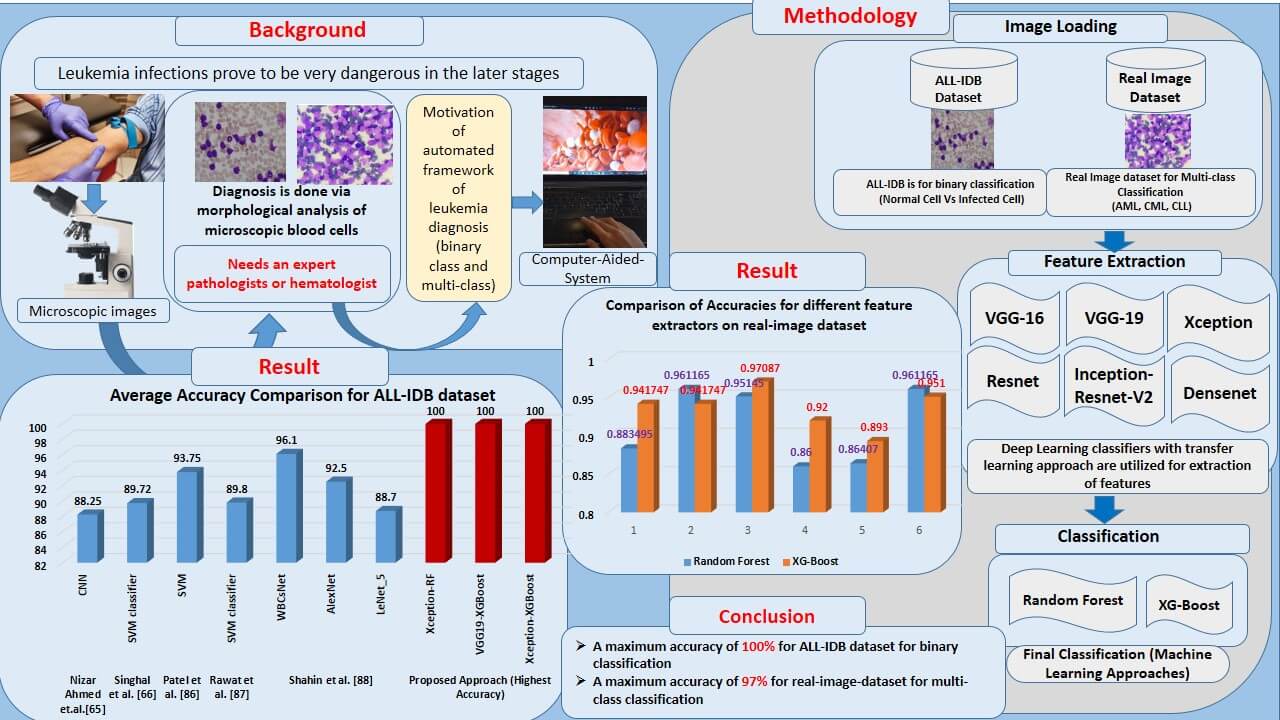
Infection of leukemia in humans causes many complications in its later stages. It impairs bone marrow’s ability to produce blood. Morphological diagnosis of human blood cells is a well-known and well-proven technique for diagnosis in this case. The binary classification is employed to distinguish between normal and leukemia-infected cells. In addition, various subtypes of leukemia require different treatments. These sub-classes must also be detected to obtain an accurate diagnosis of the type of leukemia. This entails using multi-class classification to determine the leukemia subtype. This is usually done using a microscopic examination of these blood cells. Due to the requirement of a trained pathologist, the decision process is critical, which leads to the development of an automated software framework for diagnosis. Researchers utilized state-of-the-art machine learning approaches, such as Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), Naïve Bayes, K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN), and others, to provide limited accuracies of classification. More advanced deep-learning methods are also utilized. Due to constrained dataset sizes, these approaches result in over-fitting, reducing their outstanding performances. This study introduces a deep learning-machine learning combined approach for leukemia diagnosis. It uses deep transfer learning frameworks to extract and classify features using state-of-the-art machine learning classifiers. The transfer learning frameworks such as VGGNet, Xception, InceptionResV2, Densenet, and ResNet are employed as feature extractors. The extracted features are given to RF and XGBoost classifiers for the binary and multi-class classification of leukemia cells. For the experimentation, a very popular ALL-IDB dataset is used, approaching a maximum accuracy of 100%. A private real images dataset with three subclasses of leukemia images, including Acute Myloid Leukemia (AML), Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), and Chronic Myloid Leukemia (CML), is also employed to generalize the system. This dataset achieves an impressive multi-class classification accuracy of 97.08%. The proposed approach is robust and generalized by a standardized dataset and the real image dataset with a limited sample size (520 images). Hence, this method can be explored further for leukemia diagnosis having a limited number of dataset samples.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools