 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Robust Machine Learning Technique to Classify COVID-19 Using Fusion of Texture and Vesselness of X-Ray Images
1 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, N.B.K.R. Institute of Science & Technology, Vidyanagar, Andhra Pradesh, 524413, India
2 Department of Teleinformatics Engineering, Federal University of Ceará, Fortaleza, 60455-970, Brazil
3 Information Technology Department, College of Computer and Information Sciences, Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University, Riyadh, 84428, Saudi Arabia
4 Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Zagazig University, Zagazig, 44519, Egypt
5 Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering, Galala University, Suez, 435611, Egypt
6 Artificial Intelligence Research Center (AIRC), College of Engineering and Information Technology, Ajman University, Ajman, United Arab Emirates
7 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Lebanese American University, Byblos, 13-5053, Lebanon
8 Department of Avionics, Indian Institute of Space Science and Technology, Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala, 695547, India
9 Department of Veterinary Clinical Sciences, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, Minnesota, 55108, USA
* Corresponding Authors: Shaik Mahaboob Basha. Email: ; Samia Allaoua Chelloug. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Intelligent Biomedical Image Processing and Computer Vision)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 138(2), 1981-2004. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.031425
Received 16 June 2023; Accepted 21 July 2023; Issue published 17 November 2023
Abstract
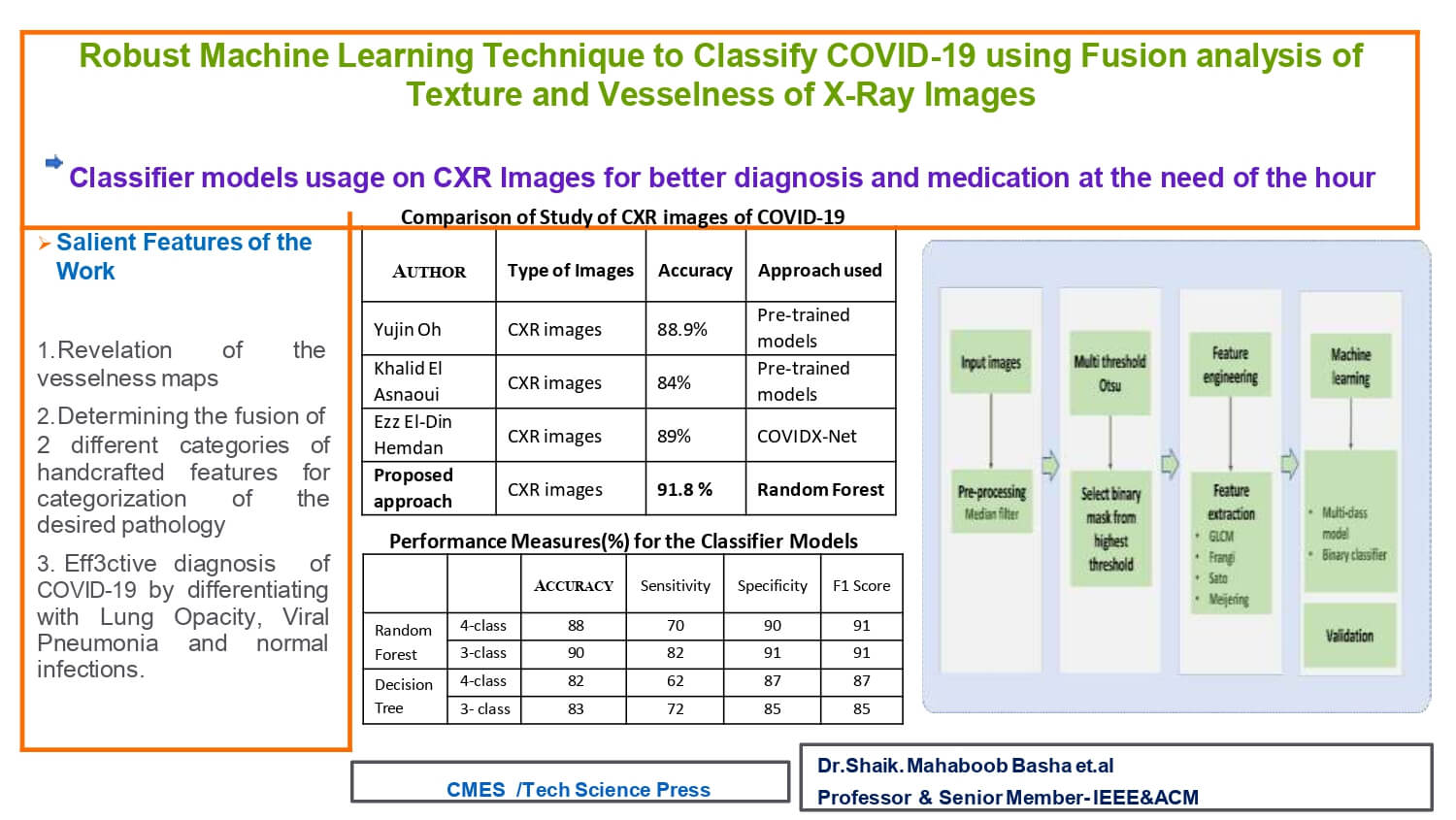
Manual investigation of chest radiography (CXR) images by physicians is crucial for effective decision-making in COVID-19 diagnosis. However, the high demand during the pandemic necessitates auxiliary help through image analysis and machine learning techniques. This study presents a multi-threshold-based segmentation technique to probe high pixel intensity regions in CXR images of various pathologies, including normal cases. Texture information is extracted using gray co-occurrence matrix (GLCM)-based features, while vessel-like features are obtained using Frangi, Sato, and Meijering filters. Machine learning models employing Decision Tree (DT) and Random Forest (RF) approaches are designed to categorize CXR images into common lung infections, lung opacity (LO), COVID-19, and viral pneumonia (VP). The results demonstrate that the fusion of texture and vessel-based features provides an effective ML model for aiding diagnosis. The ML model validation using performance measures, including an accuracy of approximately 91.8% with an RF-based classifier, supports the usefulness of the feature set and classifier model in categorizing the four different pathologies. Furthermore, the study investigates the importance of the devised features in identifying the underlying pathology and incorporates histogram-based analysis. This analysis reveals varying natural pixel distributions in CXR images belonging to the normal, COVID-19, LO, and VP groups, motivating the incorporation of additional features such as mean, standard deviation, skewness, and percentile based on the filtered images. Notably, the study achieves a considerable improvement in categorizing COVID-19 from LO, with a true positive rate of 97%, further substantiating the effectiveness of the methodology implemented.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools