 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Role Dynamic Allocation of Human-Robot Cooperation Based on Reinforcement Learning in an Installation of Curtain Wall
1 School of Control and Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin Chengjian University, Tianjin, 300384, China
2 Comprehensive Business Department, CATARC (Tianjin) Automotive Engineering Research Institute Co., Ltd., 300339, China
3 School of Mechanical Engineering, Hebei University of Technology, Tianjin, 300130, China
* Corresponding Author: Jian Zhao. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Machine Learning-Guided Intelligent Modeling with Its Industrial Applications)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2024, 138(1), 473-487. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.029729
Received 05 March 2023; Accepted 09 May 2023; Issue published 22 September 2023
Abstract
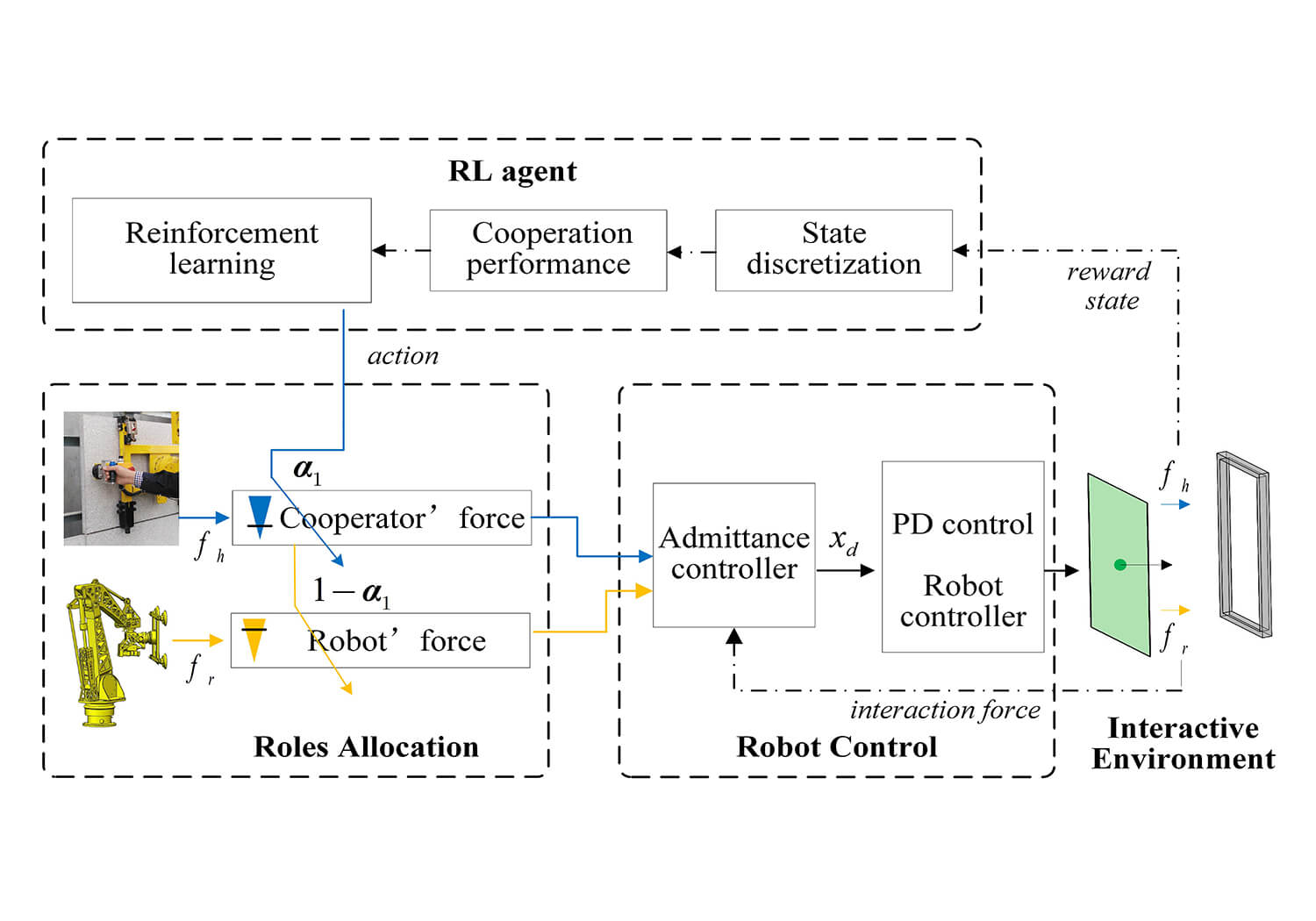
A real-time adaptive roles allocation method based on reinforcement learning is proposed to improve human-robot cooperation performance for a curtain wall installation task. This method breaks the traditional idea that the robot is regarded as the follower or only adjusts the leader and the follower in cooperation. In this paper, a self-learning method is proposed which can dynamically adapt and continuously adjust the initiative weight of the robot according to the change of the task. Firstly, the physical human-robot cooperation model, including the role factor is built. Then, a reinforcement learning model that can adjust the role factor in real time is established, and a reward and action model is designed. The role factor can be adjusted continuously according to the comprehensive performance of the human-robot interaction force and the robot’s Jerk during the repeated installation. Finally, the roles adjustment rule established above continuously improves the comprehensive performance. Experiments of the dynamic roles allocation and the effect of the performance weighting coefficient on the result have been verified. The results show that the proposed method can realize the role adaptation and achieve the dual optimization goal of reducing the sum of the cooperator force and the robot’s Jerk.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools