 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Multi Head Deep Neural Network Prediction Methodology for High-Risk Cardiovascular Disease on Diabetes Mellitus
School of Information Technology and Engineering, Vellore Institute of Technology, Vellore, Tamilnadu, 632014, India
* Corresponding Author: Kuruva Lakshmanna. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Smart and Secure Solutions for Medical Industry)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2023, 137(3), 2513-2528. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.028944
Received 18 January 2023; Accepted 20 March 2023; Issue published 03 August 2023
Abstract
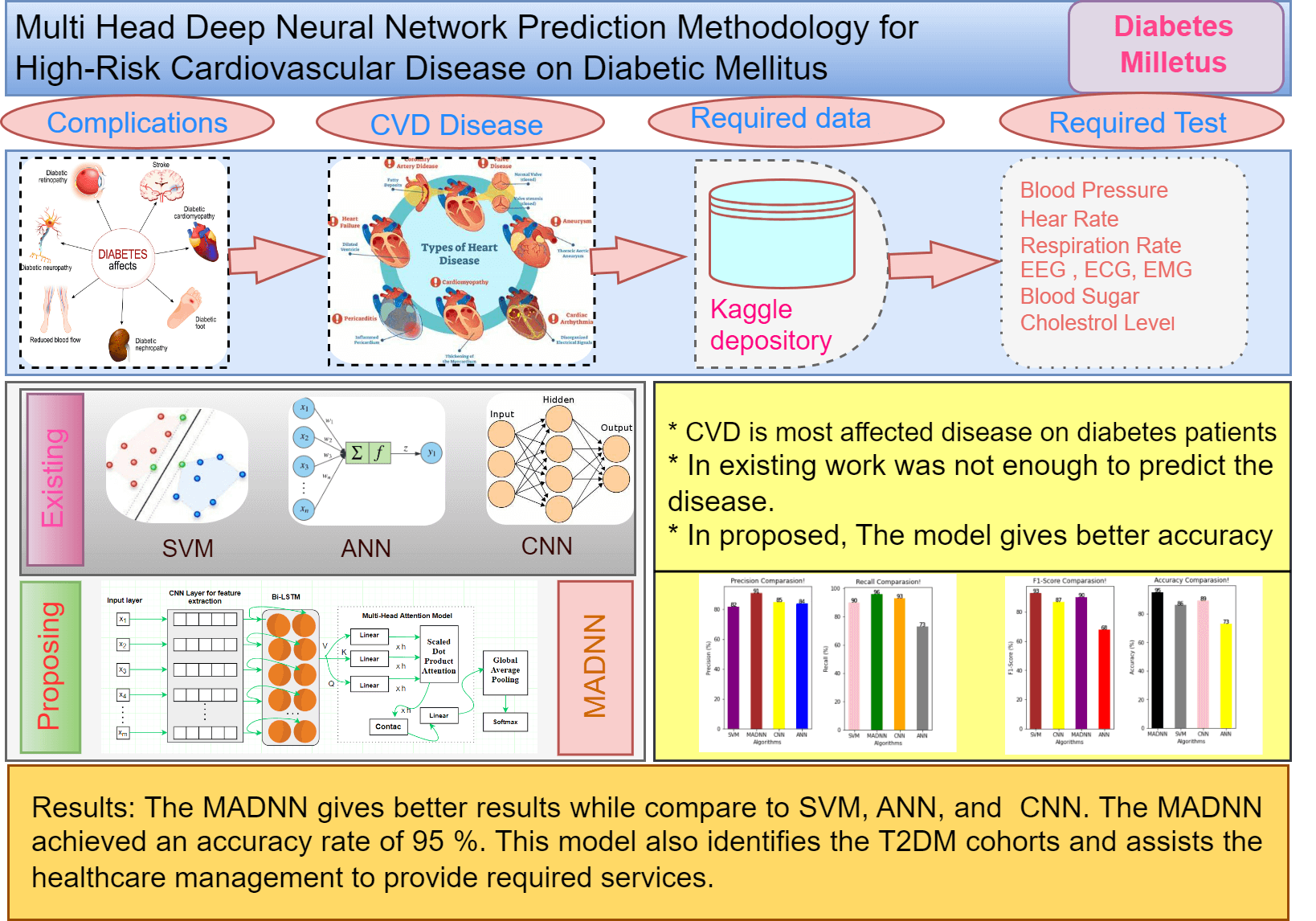
Major chronic diseases such as Cardiovascular Disease (CVD), diabetes, and cancer impose a significant burden on people and healthcare systems around the globe. Recently, Deep Learning (DL) has shown great potential for the development of intelligent mobile Health (mHealth) interventions for chronic diseases that could revolutionize the delivery of health care anytime, anywhere. The aim of this study is to present a systematic review of studies that have used DL based on mHealth data for the diagnosis, prognosis, management, and treatment of major chronic diseases and advance our understanding of the progress made in this rapidly developing field. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DMs) is a regular chronic disorder that is caused by the secretion of insulin, which leads to serious death-related issues and the most complicated ones. Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) is the most frequent issue related to T2DM patients. The major concern is recognizing the high possibility of CHD complications, yet the model is not available to identify it. This work introduces a deep learning technique that can predict heart disease effectively using a hybrid model, which integrates DNNs (Deep Neural Networks) with a Multi-Head Attention Model called MADNN. The scheme can be designed to automatically learn the best-quality features from Electronic Health Records (EHRs), and effectively combine heterogeneous and time-sequenced medical data for predicting the risk of CVD. The analysis is done using the Kaggle dataset. The outcomes prove that the MADNN has improved accuracy by about 95% and indicates the precise accuracy is higher for the disease compared with SVM, CNN and ANN.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools