 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Nonlinear Analysis of Organic Polymer Solar Cells Using Differential Quadrature Technique with Distinct and Unique Shape Function
1
Department of Engineering Mathematics and Physics, Faculty of Engineering, Zagazig University, Zagazig, 44519, Egypt
2
Basic Science Department, Faculty of Engineering, Delta University for Science and Technology, Gamasa, 11152, Egypt
3
Department of Medical Research, China Medical University Hospital, China Medical University, Taichung, 404327, Taiwan
* Corresponding Author: Omer Civalek. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2023, 137(3), 2193-2217. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.028992
Received 22 January 2023; Accepted 23 April 2023; Issue published 03 August 2023
Abstract
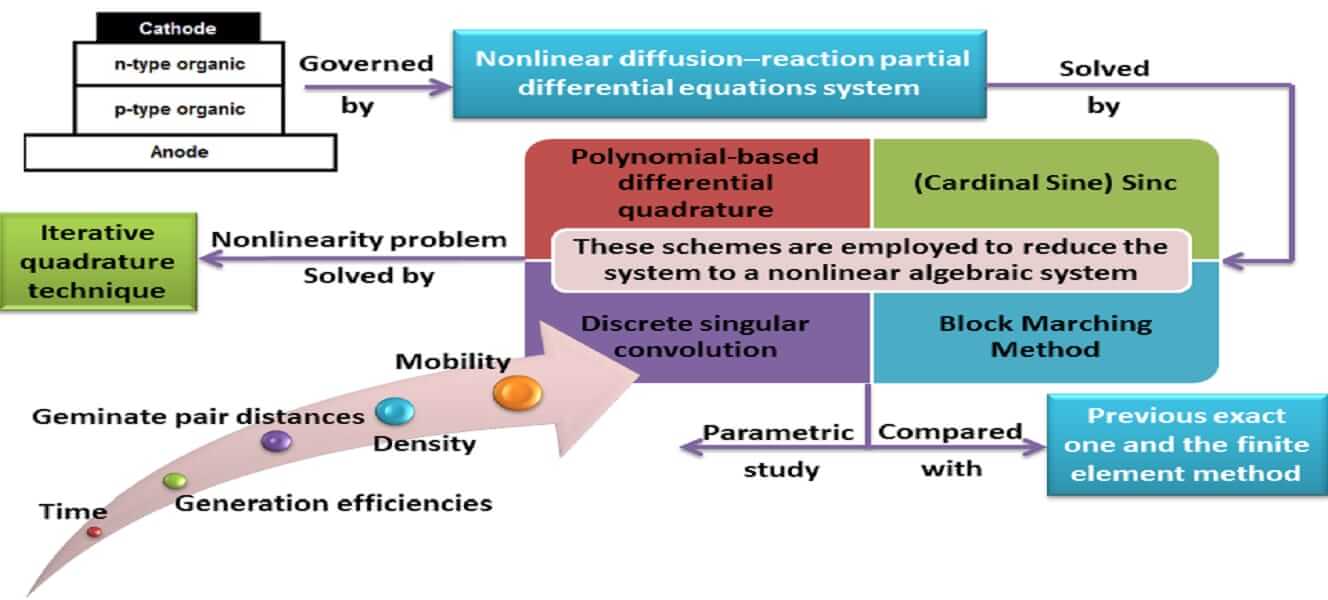
Four numerical schemes are introduced for the analysis of photocurrent transients in organic photovoltaic devices. The mathematical model for organic polymer solar cells contains a nonlinear diffusion–reaction partial differential equation system with electrostatic convection attached to a kinetic ordinary differential equation. To solve the problem, Polynomial-based differential quadrature, Sinc, and Discrete singular convolution are combined with block marching techniques. These schemes are employed to reduce the problem to a nonlinear algebraic system. The iterative quadrature technique is used to solve the reduced problem. The obtained results agreed with the previous exact one and the finite element method. Further, the effects of different times, different mobilities, different densities, different geminate pair distances, different geminate recombination rate constants, different generation efficiencies, and supporting conditions on photocurrent have been analyzed. The novelty of this paper is that these schemes for photocurrent transients in organic polymer solar cells have never been presented before, so the results may be useful for improving the performance of solar cells.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools