 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Temperature Field in Laser Line Scanning Thermography: Analytical Calculation and Experiment
1
China Aerodynamics Research and Development Center, Mianyang, 621000, China
2
Xi’an Research Institute of High Technology, Xi’an, 710025, China
3
Nanjing Novelteq, Ltd., Nanjing, 210038, China
* Corresponding Author: Bowen Liu. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Computational Models for Decision-Making of Complex Systems in Engineering)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2023, 137(1), 1001-1018. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.027072
Received 12 October 2022; Accepted 14 December 2022; Issue published 23 April 2023
Abstract
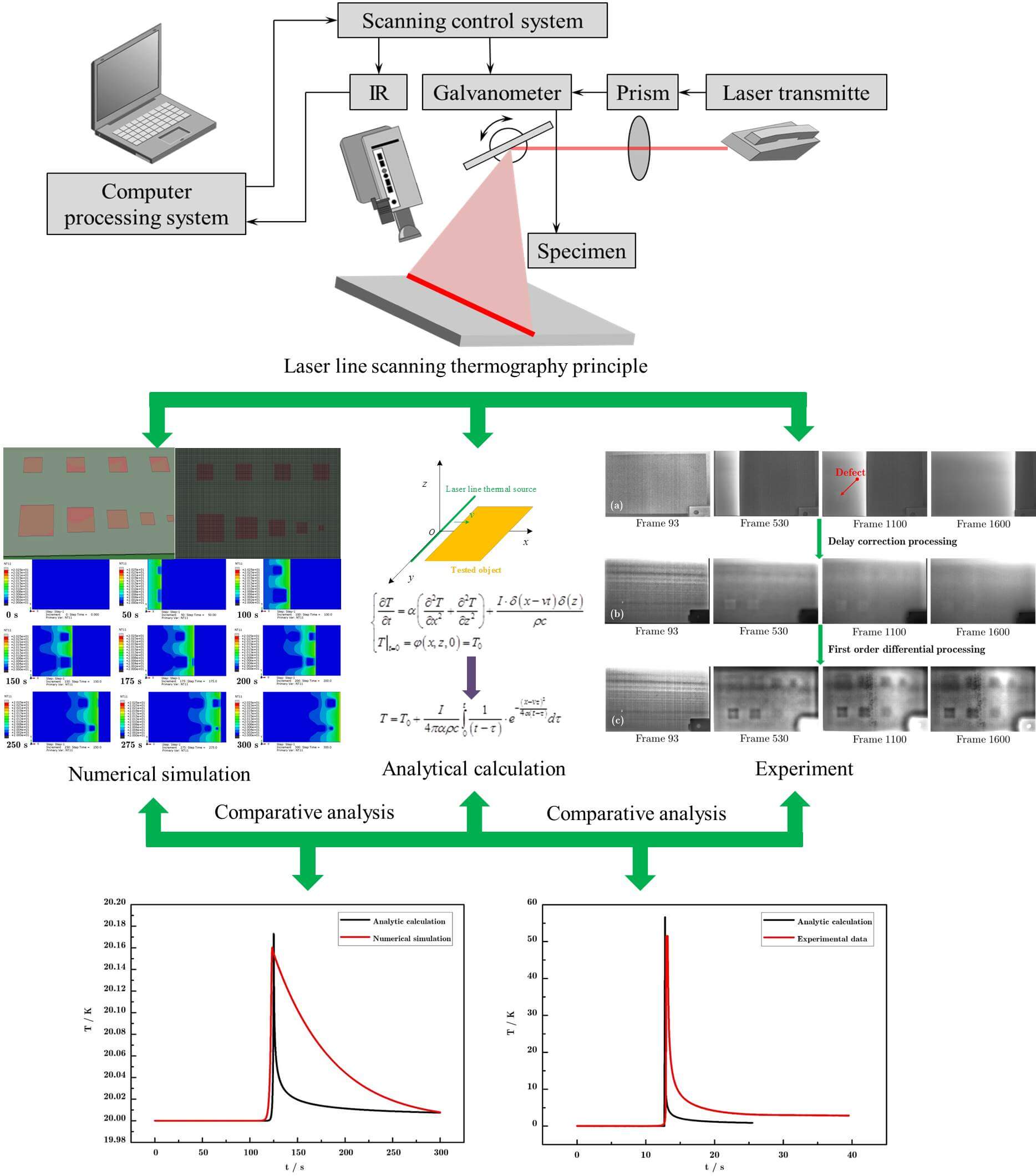
The temperature field in laser line scanning thermography is investigated comprehensively in this work, including analytical calculation and experiment. Firstly, the principle of laser line scanning thermography is analyzed. On this basis, a physical laser line scanning model is proposed. Afterwards, based on Fourier transform (FT) and segregation variable method (SVM), the heat conduction differential equation in laser line scanning thermography is derived in detail. The temperature field of the composite-based coatings model with defects is simulated numerically. The results show that the laser line scanning thermography can effectively detect the defects in the model. The correctness of the analytical calculation is verified by comparing the surface temperature distribution obtained by analytical calculation and numerical simulation. Additionally, an experiment is carried out and the changeable surface temperature obtained by analytical calculation is compared with the experimental results. It shows that the error of maximum temperature obtained by analytical calculation and by experiment is 8% with high accuracy, which proves the correctness of analytical calculation and enriches the theoretical foundation of laser line scanning thermography.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools