 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
A Novel Method to Enhance the Inversion Speed and Precision of the NMR T2 Spectrum by the TSVD Based Linearized Bregman Iteration
1 State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, Xi’an, 710069, China
2 Department of Geology, Northwest University, Xi’an, 710069, China
3 Reseach Institute of Shaanxi Yanchang Petroleum (Group) Co., Ltd., Xi’an, 710075, China
4 School of Geosciences, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao, 266580, China
* Corresponding Author: Yiguo Chen. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Modeling of Fluids Flow in Unconventional Reservoirs)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2023, 136(3), 2451-2463. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2023.021145
Received 29 December 2021; Accepted 29 November 2022; Issue published 09 March 2023
Abstract
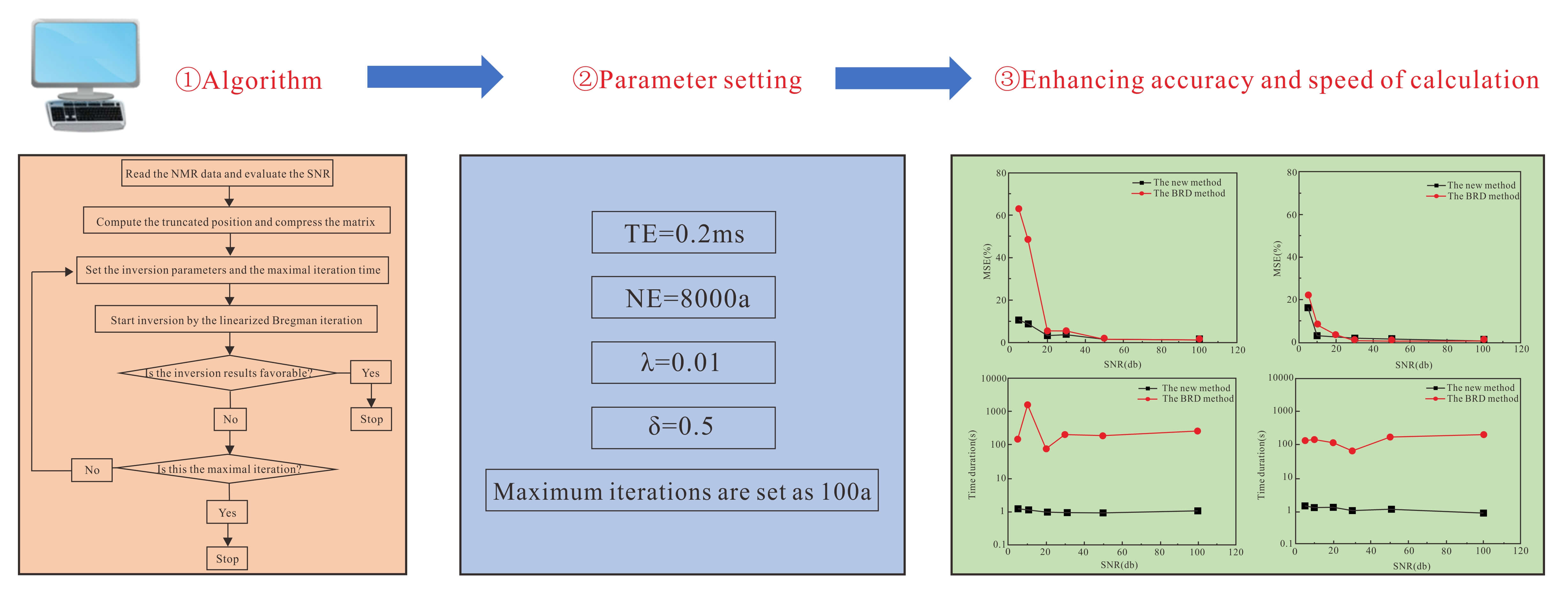
The low-field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technique has been used to probe the pore size distribution and the fluid composition in geophysical prospecting and related fields. However, the speed and accuracy of the existing numerical inversion methods are still challenging due to the ill-posed nature of the first kind Fredholm integral equation and the contamination of the noises. This paper proposes a novel inversion algorithm to accelerate the convergence and enhance the precision using empirical truncated singular value decompositions (TSVD) and the linearized Bregman iteration. The L1 penalty term is applied to construct the objective function, and then the linearized Bregman iteration is utilized to obtain fast convergence. To reduce the complexity of the computation, empirical TSVD is proposed to compress the kernel matrix and determine the appropriate truncated position. This novel inversion method is validated using numerical simulations. The results indicate that the proposed novel method is significantly efficient and can achieve quick and effective data solutions with low signal-to-noise ratios.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools