 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
CEMA-LSTM: Enhancing Contextual Feature Correlation for Radar Extrapolation Using Fine-Grained Echo Datasets
1
School of Computer and Software, Engineering Research Center of Digital Forensics, Ministry of Education, Nanjing University
of Information Science and Technology, Nanjing, 210044, China
2
School of Computing, Edinburgh Napier University, Edinburgh, EH10 5DT, UK
3
School of Automation, Nanjing University of Information Science Technology, Nanjing, 210044, China
* Corresponding Author: Qi Liu. Email:
# Both are the first authors due to their equal contributions
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2023, 135(1), 45-64. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2022.022045
Received 18 February 2022; Accepted 24 May 2022; Issue published 29 September 2022
Abstract
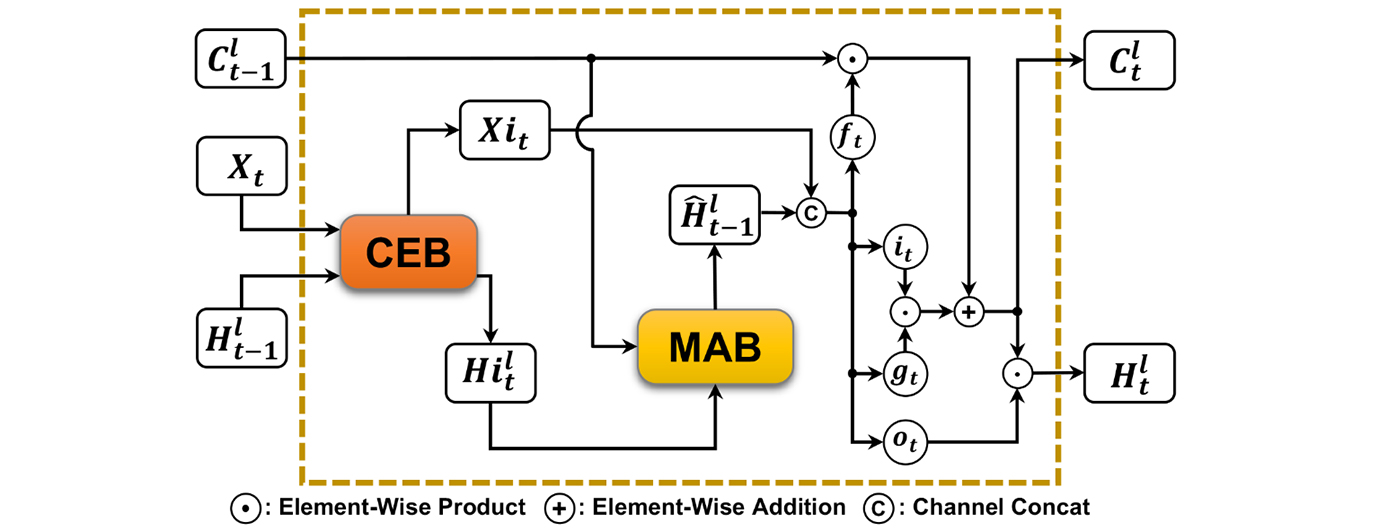
Accurate precipitation nowcasting can provide great convenience to the public so they can conduct corresponding arrangements in advance to deal with the possible impact of upcoming heavy rain. Recent relevant research activities have shown their concerns on various deep learning models for radar echo extrapolation, where radar echo maps were used to predict their consequent moment, so as to recognize potential severe convective weather events. However, these approaches suffer from an inaccurate prediction of echo dynamics and unreliable depiction of echo aggregation or dissipation, due to the size limitation of convolution filter, lack of global feature, and less attention to features from previous states. To address the problems, this paper proposes a CEMA-LSTM recurrent unit, which is embedded with a Contextual Feature Correlation Enhancement Block (CEB) and a Multi-Attention Mechanism Block (MAB). The CEB enhances contextual feature correlation and supports its model to memorize significant features for near-future prediction; the MAB uses a position and channel attention mechanism to capture global features of radar echoes. Two practical radar echo datasets were used involving the FREM and CIKM 2017 datasets. Both quantification and visualization of comparative experimental results have demonstrated outperformance of the proposed CEMA-LSTM over recent models, e.g., PhyDNet, MIM and PredRNN++, etc. In particular, compared with the second-ranked model, its average POD, FAR and CSI have been improved by 3.87%, 1.65% and 1.79%, respectively on the FREM, and by 1.42%, 5.60% and 3.16%, respectively on the CIKM 2017.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools