 | Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences |  |
DOI: 10.32604/cmes.2022.022103
ARTICLE
Some Properties of Degenerate r-Dowling Polynomials and Numbers of the Second Kind
1Department of Mathematics Education, Daegu Catholic University, Gyeongsan, 38430, Korea
2School of Electronic and Electric Engineering, Daegu University, Gyeongsan, 38453, Korea
*Corresponding Author: Hye Kyung Kim. Email: hkkim@cu.ac.kr
Received: 21 February 2022; Accepted: 11 May 2022
Abstract: The generating functions of special numbers and polynomials have various applications in many fields as well as mathematics and physics. In recent years, some mathematicians have studied degenerate version of them and obtained many interesting results. With this in mind, in this paper, we introduce the degenerate r-Dowling polynomials and numbers associated with the degenerate r-Whitney numbers of the second kind. We derive many interesting properties and identities for them including generating functions, Dobinski-like formula, integral representations, recurrence relations, differential equation and various explicit expressions. In addition, we explore some expressions for them that can be derived from repeated applications of certain operators to the exponential functions, the derivatives of them and some identities involving them.
Keywords: Dowling lattice; Whitney numbers and polynomials; r-Whitney numbers and polynomials of the second kind; r-Bell polynomials; r-Stirling numbers; dowling numbers and polynomials
Mathematics Subject Classification: 11F20; 11B68; 11B83
The Stirling number
When
Dowling [2] constructed a certain lattice for a finite group of order m, called Dowling lattice, and using the Möbius function, he introduced the corresponding Whitney numbers of the first kind
For
As a generalization of the the Whitney numbers
and
respectively, for
When
We note that
Note that the
The r-Whitey numbers of both kinds and r-Dowling polynomials were studied by several authors. The references [2–5,7–15] provided readers more information. In particular, Cheon et al. [8] and Corcino et al. [11] gave combinatorial interpretations of the r-Whitney numbers of the first and second kind, respectively. In recently years, many mathematicians have been studied the degenerate special polynomials and numbers, and have obtained many interesting results [14,16–24]. In particular, the generating functions of (degenerate) special numbers and polynomials have various applications in many fields as well as mathematics and physics [1–32]. Kim et al. [14] introduced the degenerate Whitney numbers of the first kind and the second kind of Dowling lattice
and
With these in mind, we naturally introduce the degenerate r-Dowling polynomials and numbers associated with the degenerate r-Whitney numbers
In this section, we introduce the basic definitions and properties of the degenerate r-Dowling polynomials and numbers needed in this paper.
For
Cheon et al. [8] introduced the r-Dowling polynomials associated with the r-Whitney numbers
By (1) and (4), the generating function of r-Dowling polynomials is given by
where
Corcino et al. [11] studied asymptotic formulas for r-Whitney numbers of the second kind with integer and real parameters. They also obtained the range of validity of each formula.
As is well known, for any
where
The degenerate Stirling numbers of the second kind are given by
Kim et al. studied the unsigned degenerate r-Stirling numbers of the second kind defined by
From (7), the generating function of the degenerate r-Stirling numbers of the second kind is given by
where j is a non-negative integer.
In view of (8), the degenerate r-Bell polynomials are given by
From (9), it is easy to show that the generating function of degenerate r-Bell polynomials is given by
when
Kim et al. introduced the
From (11), we easily get
From (12), we note that
3 Degenerate r-Dowling Polynomials and Numbers
In this section, we explore various properties for the degenerate r-Dowling polynomials and numbers.
From (1), the degenerate r-Whitney numbers
Lemma 3.1. [14] For
In Lemma 3.1, when
From Lemma 3.1, (6) and (8), we get
The next theorem is a recurrence relation of the degenerate Whitney numbers of the second kind.
Theorem 3.1. For
Proof. From (14), we observe that
By comparing the coefficients of both sides of (16), we get the desired recurrence relation.
The following theorem shows that the degenerate r-Whitney numbers of second kind expresses the finite sum of degenerate falling factorials.
Theorem 3.2. For
Proof. By (5) and Lemma 3.1, we observe that
By comparing the coefficients of both sides of (17), we get the desired result.
In Theorem 3.2, when
In this paper, we naturally consider the degenerate
When
When
When
Theorem 3.3. For
Proof. From Lemma 3.1 and (18), we observe that
By (19), we have the generating function of degenerate r-Dowling polynomials of the second kind.
When
When
Theorem 3.4. (Dobinski-like formula)
For
When
Proof. From (5) and Theorem 3.3, we note that
By comparing the coefficients of both sides of (20), we have Dobinski-like formula for the degenerate r-Dowling polynomials.
In the following theorem and corollary, we have integral representations of the degenerate r-Whitney numbers and the degenerate r-Dowling polynomials, respectively.
Theorem 3.5. For
where
Proof. From Lemma 3.1, we get
Therefore, by (21) we have the desired result.
Corollary 3.1. For
Proof. By Lemma 3.1 and Theorem 3.5, we have
From (22), we get the desired identity.
Lemma 3.2. For
Proof. From Theorem 3.2 and (13), we get
By (23), we obtain the desired result.
The next theorem is a recurrence relation of degenerate r-Dowling polynomials.
Theorem 3.6. For
Proof. From (18) and Lemma 3.2, we have
Here
Theorem 3.7. For
Proof. For
By comparing the coefficients of both sides of (25), we get what we want.
The following theorem is another recurrence relation of degenerate r-Dowling polynomials.
Theorem 3.8. For
Proof. From Theorem 3.3, we note that
On the other hand, by (26), we get
By comparing the coefficients of (26) with (27), we get the desired identity.
Remark. When
Next, we explore two identities including degenerate r-Dowling polynomials that can be derived from repeated applications of certain operators to the degenerate exponential functions.
Theorem 3.9. For
Proof. First, we observe that
By (29) and Theorem 3.4,
From (30), we have what we want.
Let
By Theorem 3.3, we have
From (31), the generating function of
Theorem 3.10. For
Proof. Let
By (33), we get
By (34), we attain the desired result.
Remark. When
In Theorem 3.1, when
From (35), we obtain
In (35), when
From (36),
In (35), when
From (37), we get
Thus, by (38), we have
In the same way, we get
By continuous this process, we get all the r-Dowling numbers
As you can see from (39), the larger n, the more difficult it is to calculate by hand. Here we use Mathematica and Fortran language to find these values.
In Fig. 1, when

Figure 1: D(2) = D5,r,λ(2), when λ = 0.1 and 0.5, respectively
In Fig. 2, when

Figure 2: D(3) = D5,r,λ(3), when λ = 0.1 and 0.5, respectively
In Fig. 3, when
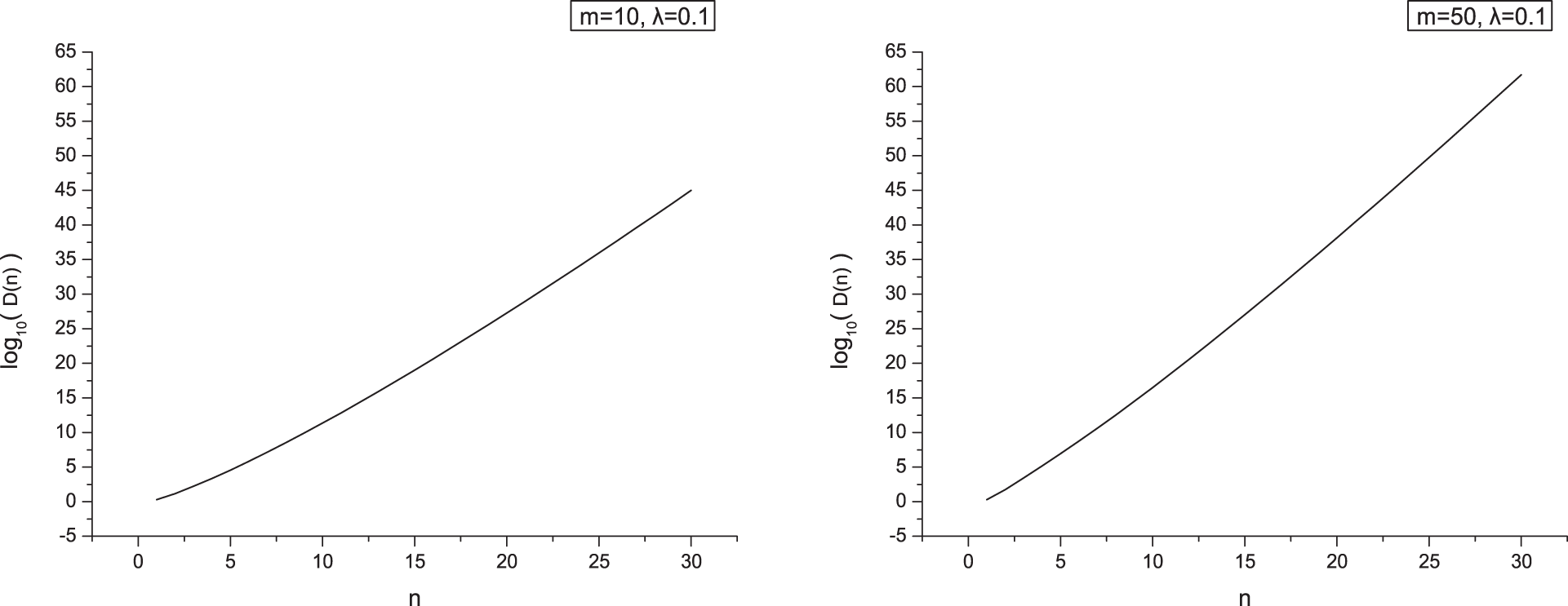
Figure 3: log10(D(n)) = log10(Dm,1,0.1(n)) when m = 10 and 50, respectively
In Fig. 4, when
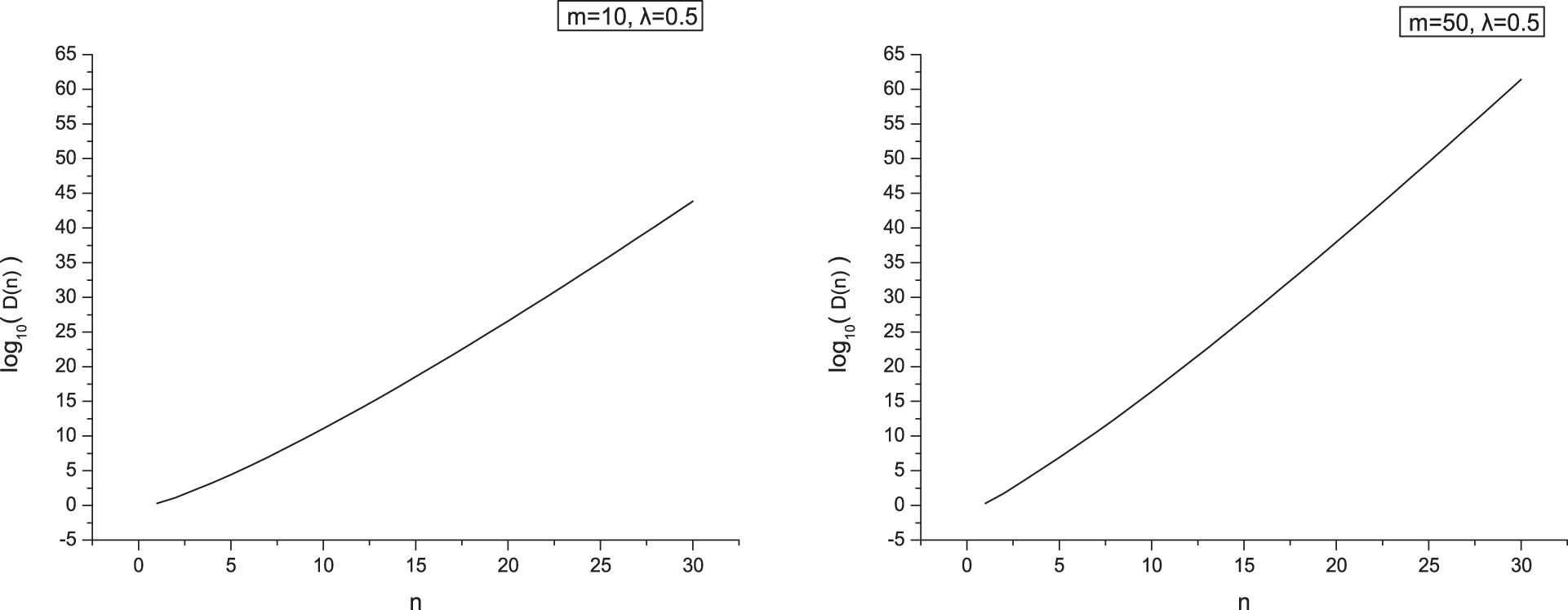
Figure 4: log10(D(n)) = log10(Dm,1,0.5(n)) when m = 10 and 50, respectively
Next, we can get differential equation for degenerate r-Dowling polynomials as follows:
Theorem 3.11. For
Proof. By using Theorem 3.4, we observe
On the other hand, we have
From (42), we get
By (43), we obtain the desire result.
Now, we study the derivative of degenerate r-Dowling polynomials
Theorem 3.12. For
Proof. From (5) and Theorem 3.3, we observe that
By comparing the coefficients on both sides of (44), we attain the desired identity.
Theorem 3.13. For
Proof. From (5) and Theorem 3.3, we have
From (45), we observe that
By (46), we have
From (47), we obtain
By comparing the coefficients of both sides of (45), we have the desired identity.
If we put
Theorem 3.14. For
Proof. Let
Thus, by (49), we have
From (50), we attain the desired formula.
In this paper, we studied many interesting properties for the degenerate r-Dowling polynomials and numbers associated with the degenerate r-Whitney numbers of the second kind. Among these identity expressions, we obtained the generating function in Theorem 3.3, Dobinski-like formula in Theorem 3.4, recurrence relations in Theorem 3.6 and 3.8, differential equation in Theorem 3.11, the derivatives of them in Theorem 3.12 for r-Dowling polynomials of the second kind. In particular, we obtained some expressions for them that can be derived from repeated applications of certain operators to the exponential functions in Theorem 3.9, 3.10 and 3.14, and some identities involving integration in Theorem 3.13. Furthermore, we found that all exact values of all r-Dowling numbers of the second kind can be obtained using (28). As a follow-up study of this paper, we can explore truncated degenerate r-Dowling polynomials and degenerate r-Dowling polynomials arising from
Acknowledgement: The author would like to thank the referees for the detailed and valuable comments that helped improve the original manuscript in its present form. Also, the authors thank Jangjeon Institute for Mathematical Science for the support of this research.
Authors’ Contributions: HKK structured and wrote the whole paper. DSL performed computer simulations in the paper. All authors checked the results of the paper and completed the revision of the article.
Consent for Publication: The authors want to publish this paper in this journal.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate: The authors declare that there is no ethical problem in the production of this paper.
Funding Statement: This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2021R1F1A1050151).
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to report regarding the present study.
References
1. Comtet, L. (1974). Advanced combinatorics: The art of finite and infinite expansions. Dordrecht: Reidel. [Google Scholar]
2. Dowling, T. A. (1973). A class of gemometric lattices bases on finite groups. Journal of Combinatorics Theory Series B, 14, 61–86. DOI 10.1016/S0095-8956(73)80007-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
3. Benoumhani, M. (1996). On Whitney numbers of Dowling lattices. Discrete Mathathematics, 159, 13–33. DOI 10.1016/0012-365X(95)00095-E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
4. Benoumhani, M. (1997). On some numbers related to Whitney numbers of Dowling lattices. Advanced Applied Matathematics, 19, 106–116. DOI 10.1006/aama.1997.0529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
5. Mezö, I. (2010). A new formula for the Bernoulli polynomials. Results Mathmathematics, 58, 329–335. DOI 10.1007/s00025-010-0039-z. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
6. Ruciński, A., Voigt, B. (1990). A local limit theorem for generalized Stirling numbers. Revue Roumaine de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées, 35(2), 161–172. [Google Scholar]
7. Corcino, R. B., Corcino, C. B., Aldema, R. (2006). Asymptotic normality of the (r, β)-Stirling numbers. Ars Combinbinatorics, 81, 81–96. [Google Scholar]
8. Cheon, G. S., Jung, J. H. (2012). r-Whitney numbers of dowling lattices. Discrete Mathematics, 312(15), 2337–2348. DOI 10.1016/j.disc.2012.04.001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
9. Cillar, J. A. D., Corcino, R. B. (2020). A q-analogue of Qi formula for r-Dowling numbers. Communications of the Korean Mathematical Society, 35(1), 21–41. DOI 10.4134/CKMS.c180478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
10. Cheon, G. S., El-Mikkawy, M. E. A. (2008). Generalized harmonic numbers with Riordan arrays. Journal of Number Theory, 128, 413–425. DOI 10.1016/j.jnt.2007.08.011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
11. Corcino, C. B., Corcino, R. B., Acala, N. (2014). Asymptotic estimates for r-Whitney numbers of the second kind. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 2014(2), 1–7. DOI 10.1155/2014/354053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
12. Gyimesi, E., Nyul, G. (2018). A comprehensive study of r-Dowling polynomials. Aequationes Mathematics, 92(3), 515–527. DOI 10.1007/s00010-017-0538-z. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
13. Gyimesi, E., Nyul, G. (2019). New combinatorial interpretations of r-Whitney and r-Whitney-Lah numbers. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 255, 222–233. DOI 10.1016/j.dam.2018.08.020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
14. Kim, T., Kim, D. S. (2021). A study on degenerate Whitney numbers of the first and second kinds of dowling lattices. arXiv:2013.08904, 22. (To appear Russian Journal of Mathematical Physics). DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2103.08904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
15. Simsek, Y. (2013). Generating functions for generalized Stirling type numbers, array type polynomials, Eulerian type polynomials and their applications. Fixed Point Theory and Applications, 2013, 87. DOI 10.1186/1687-1812-2013-87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
16. Carlitz, L. (1979). Degenerate Stirling, Bernoulli and Eulerian numbers. Utilitas Mathematica, 15, 51–88. [Google Scholar]
17. Lee, C. J., Kim, D. S., Kim, H., Kim, T., Lee, H. (2021). Study of degenerate poly-Bernoulli polynoials by λ-Umbral calculus. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 129(1), 393–408. DOI 10.32604/cmes.2021.016917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
18. Kim, D. S., Kim, T. (2020). A note on a new type of degenerate Bernoulli numbers. Russian Journal of Mathematical Physics, 27(2), 227–235. DOI 10.1134/S1061920820020090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
19. Kim, T. (2017). A note on degenerate Stirling polynomials of the second kind. Proceeding of Jangjeon Mathematical Society, 20(3), 319–331. DOI 10.48550/arXiv.1704.02290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
20. Kim, T., Kim, D. S., Lee, H., Kwon, J. (2020). Degenerate binoial coefficients and degenerate hypergeometric functions. Advances in Difference Equations, 2020(115), 17. DOI 10.1186/s13662-020-02575-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
21. Kim, T., Kim, D. S., Lee, H., Park, S., Kwon, J. (2021). New properties on degenerate Bell polynomials. Complexity, 2021, 13. DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2108.06260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
22. Kim, T., Kim, D. S., Lee, H., Park, J. W. (2020). A note on degenerate r-Stirling numbers. Journal of Inequalities and Applications, 2020(4), 521–531. DOI 10.1186/s13660-020-02492-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
23. Ma, Y., Kim, T., Lee, H., Kim, D. S. (2021). Some identities of fully degenerate dowling and fully degenerate Bell polynomials arising from λ-umbral calculus. arXiv:2108.11090v1. DOI 10.48550/arXiv.2108.11090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
24. Muhiuddin, G., Khan, W. A., Muhyi, A., Al-Kadi, D. (2021). Some results on type 2 degenerate poly-fubini polynomials and numbers. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 129(2), 1051–1073. DOI 10.32604/cmes.2021.016546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
25. Wania, A., Choi, J. S., (2022). Truncated exponential based Frobenius-Genocchi and truncated exponential based Apostol type Frobenius-Genocchi polynomials. Montes Taurus Journal of Pure Applied Mathematics, 4(1), 85–96. [Google Scholar]
26. Broder, A. Z. (1984). The r-Stirling numbers. Discrete Mathematics, 49, 241–259. DOI 10.1016/0012-365X(84)90161-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
27. Cvijoveć, D. (2011). New identities for the partial Bell polynomials. Applied Mathematics Letters, 24, 1544–1547. DOI 10.1016/j.aml.2011.03.043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
28. Kim, D. S., Kim, T., Jang, L. C., Kim, H. K., Kwon, J. (2022). Arithmetic of Sheffer sequences arising from Riemann, Volkenborn and Kim integrals. Montes Taurus Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 4(1), 149–169. [Google Scholar]
29. Kim, T., Kim, D. S. (2020). A note on central Bell numbers and polynomials. Russian Journal of Mathematical Physics, 27(1), 76–81. DOI 10.1134/S1061920820010070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
30. Kim, T., Kim, D. S., Dolgy, D. V., Lee, S., Kwon, J. (2021). Some identities of the higher-order type 2 Bernoulli numbers and polynomials of the second kind. Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences, 128(3), 1121–1132. DOI 10.32604/cmes.2021.016532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
31. Simsek, Y. (2019). Explicit formulas for p-adic integrals: Approach to p-adic distributions and somed families of special numbers and polynomials. Montes Taurus Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics, 1(1), 1–76. DOI 10.48550/arXiv.1910.09296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
32. Kim, T., Kim, D. S., Jang, L. C., Lee, H., Kim, H. (2022). Representations of degenerate Hermite polynomials. Advances in Applied Mathematics, 139, 102359. DOI 10.1016/j.aam.2022.102359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
