 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Radiative Flow of Ag-Fe3O4/Water Hybrid Nanofluids Induced by a Shrinking/Stretching Disk with Influence of Velocity and Thermal Slip Conditions
1 Institute of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Sindh, Jamshoro Sindh, 76080, Pakistan
2 KCAMS Khairpur Mir’s, Sindh Agriculture University, Tandojam Sindh, 70060, Pakistan
3 Department of Economics, College of Business Administration, King Saud University, Riyadh, 145111, Saudi Arabia
4 Department of Mathematics, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and Technical Sciences, Saveetha University, Chennai, 602105, India
5 Department of Mathematics, Faculty of Science, Sakarya University, Serdivan/Sakarya, 54050, Turkey
* Corresponding Author: Umair Khan. Email:
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 143(1), 499-513. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2025.061804
Received 03 December 2024; Accepted 13 February 2025; Issue published 11 April 2025
Abstract
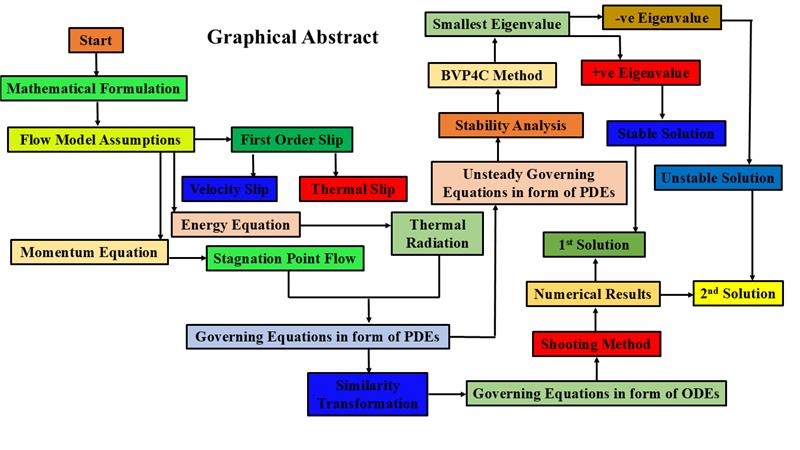
This paper discusses the model of the boundary layer (BL) flow and the heat transfer characteristics of hybrid nanofluid (HNF) over shrinking/stretching disks. In addition, the thermal radiation and the impact of velocity and thermal slip boundary conditions are also examined. The considered hybrid nano-fluid contains silver (Ag) and iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles dispersed in the water to prepare the Ag-Fe3O4/water-based hybrid nanofluid. The requisite posited partial differential equations model is converted to ordinary differential equations using similarity transformations. For a numerical solution, the shooting method in Maple is employed. Moreover, the duality in solutions is achieved for both cases of the disk (stretching () and shrinking ()). At the same time, a unique solution is observed for = 0. No solution is found for them at , whereas the solutions are split at the . Besides, the value of the is dependent on the . Meanwhile, the values of and intensified with increasing . Stability analysis has been applied using bvp4c in MATLAB software due to a dual solution. Furthermore, analysis shows that the first solution is stable and feasible physically. For the slip parameters, an increase in the velocity slip parameter increases the velocity and shear stress profiles while increasing the temperature profile in the first solutions. While the rise in thermal slip parameter reduces the temperature profile nanoparticle volume fractions increase it.Graphic Abstract
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools