 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Medical Diagnosis Based on Multi-Attribute Group Decision-Making Using Extension Fuzzy Sets, Aggregation Operators and Basic Uncertainty Information Granule
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Egaleo Park Campus, University of West Attica, Athens, 12243, Greece
* Corresponding Author: Anastasios Dounis. Email:
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advanced Computational Intelligence Techniques, Uncertain Knowledge Processing and Multi-Attribute Group Decision-Making Methods Applied in Modeling of Medical Diagnosis and Prognosis)
Computer Modeling in Engineering & Sciences 2025, 142(1), 759-811. https://doi.org/10.32604/cmes.2024.057888
Received 30 August 2024; Accepted 24 October 2024; Issue published 17 December 2024
Abstract
Accurate medical diagnosis, which involves identifying diseases based on patient symptoms, is often hindered by uncertainties in data interpretation and retrieval. Advanced fuzzy set theories have emerged as effective tools to address these challenges. In this paper, new mathematical approaches for handling uncertainty in medical diagnosis are introduced using q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets (q-ROFS) and interval-valued q-rung orthopair fuzzy sets (IVq-ROFS). Three aggregation operators are proposed in our methodologies: the q-ROF weighted averaging (q-ROFWA), the q-ROF weighted geometric (q-ROFWG), and the q-ROF weighted neutrality averaging (q-ROFWNA), which enhance decision-making under uncertainty. These operators are paired with ranking methods such as the similarity measure, score function, and inverse score function to improve the accuracy of disease identification. Additionally, the impact of varying q-rung values is explored through a sensitivity analysis, extending the analysis beyond the typical maximum value of 3. The Basic Uncertain Information (BUI) method is employed to simulate expert opinions, and aggregation operators are used to combine these opinions in a group decision-making context. Our results provide a comprehensive comparison of methodologies, highlighting their strengths and limitations in diagnosing diseases based on uncertain patient data.Graphic Abstract
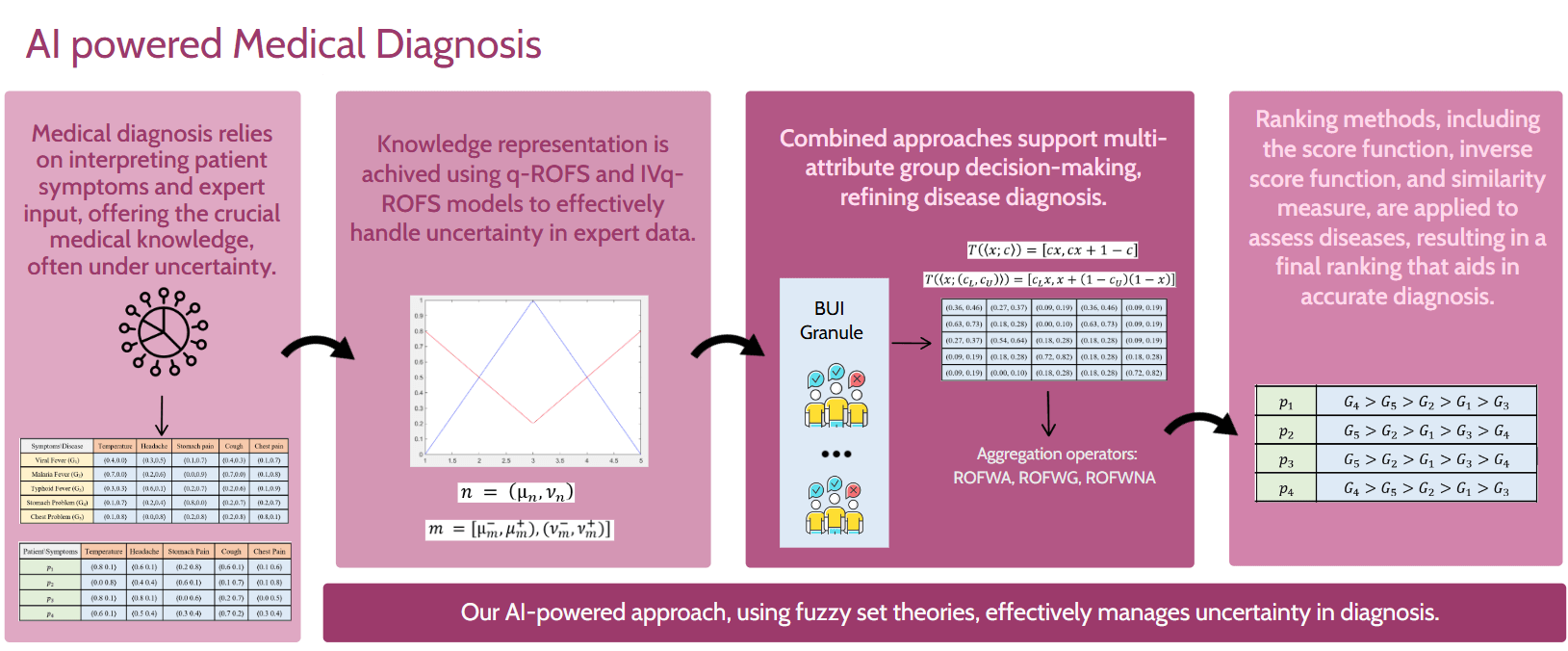
Keywords
Cite This Article
 Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Tech Science Press.This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.


 Submit a Paper
Submit a Paper Propose a Special lssue
Propose a Special lssue View Full Text
View Full Text Download PDF
Download PDF Downloads
Downloads
 Citation Tools
Citation Tools