The Journal of Renewable Materials (JRM) is an interdisciplinary journal publishing original research covering all aspects of renewable materials, namely bio-based materials, sustainable materials, green chemistry and including recycling and recovery of spent materials. The scope of the journal is devoted to reports of new and original experimental and theoretical research in the areas of materials, engineering, physics, bioscience, processing, environmental science and chemistry, which are related to renewable materials and their applications.
Ei Compendex/Engineering Village (Elsevier); Scopus Citescore (Impact per Publication 2024): 4.9; SNIP (Source Normalized Impact per Paper 2024): 0.592; Google Scholar h5-index 31, ranking 5 in Wood Science &Technology; Chemical Abstracting Services; Polymer Library; Baidu Xueshu (China); Portico, etc...
Notice: Please make new submissions of JRM to the new system (ScholarOne) (https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/jrenewmater) from 25 September 2024. To view your previous submissions, please access TSP system (https://ijs.tspsubmission.com/homepage).
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0179 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable and Biosourced Adhesives-2023)
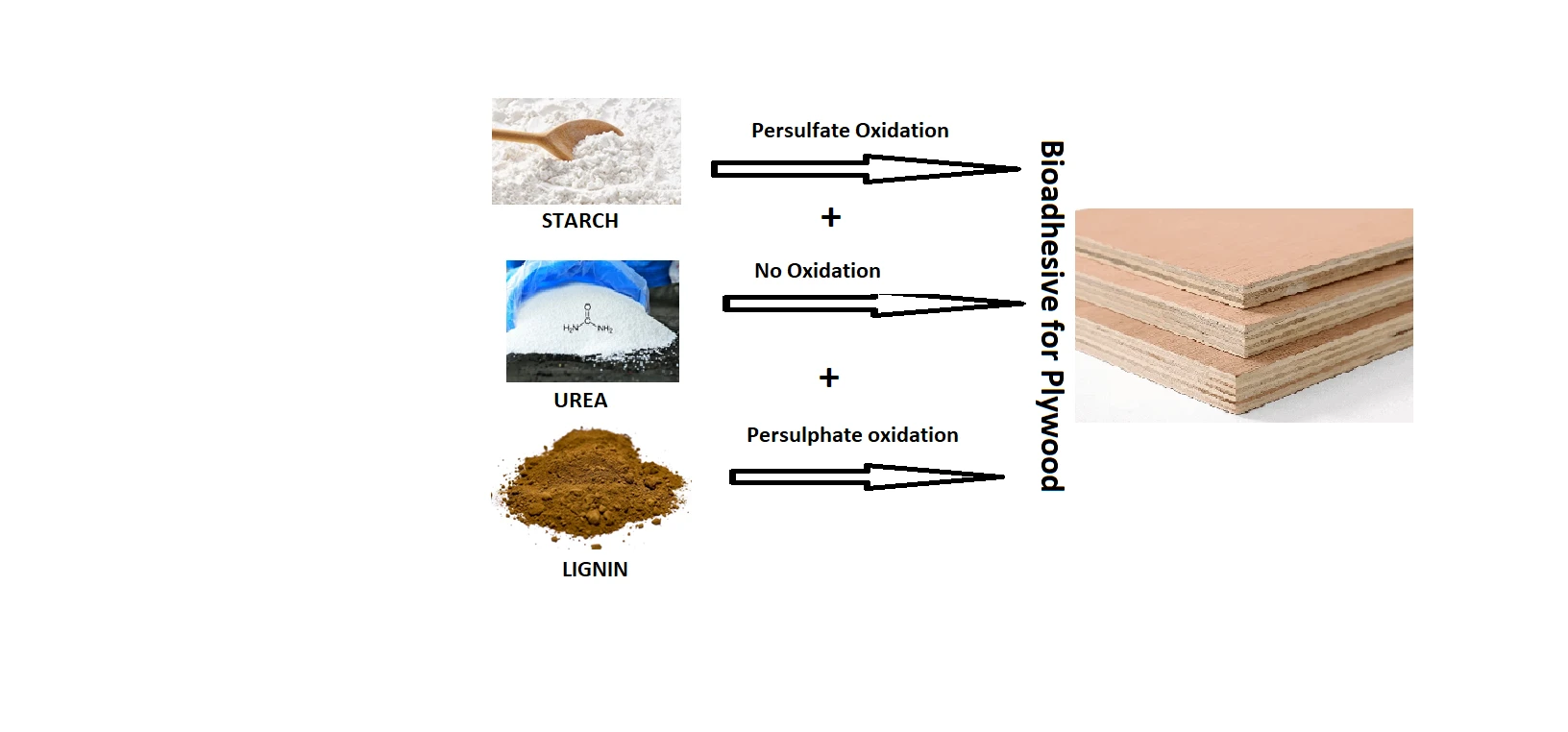
Abstract The aim of this research was to synthesize a new totally bio wood adhesive entailing the use of oxidized starch (OST), urea, and oxidized lignin (OL). For this reason, non-modified (L) and oxidized lignin (OL) at different contents (20%, 30%, and 40%) were used to prepare the starch-urea-lignin (SUL) and starch-urea-oxidized lignin (SUOL) resin. Sodium persulfate (SPS) as oxidizer was employed to oxidize both starch and lignin. Urea was just used as a low cost and effective crosslinker in the resin composition. The properties of the synthesized resins and the plywood panels bonded with them… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0181 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Renewable and Biosourced Adhesives-2023)
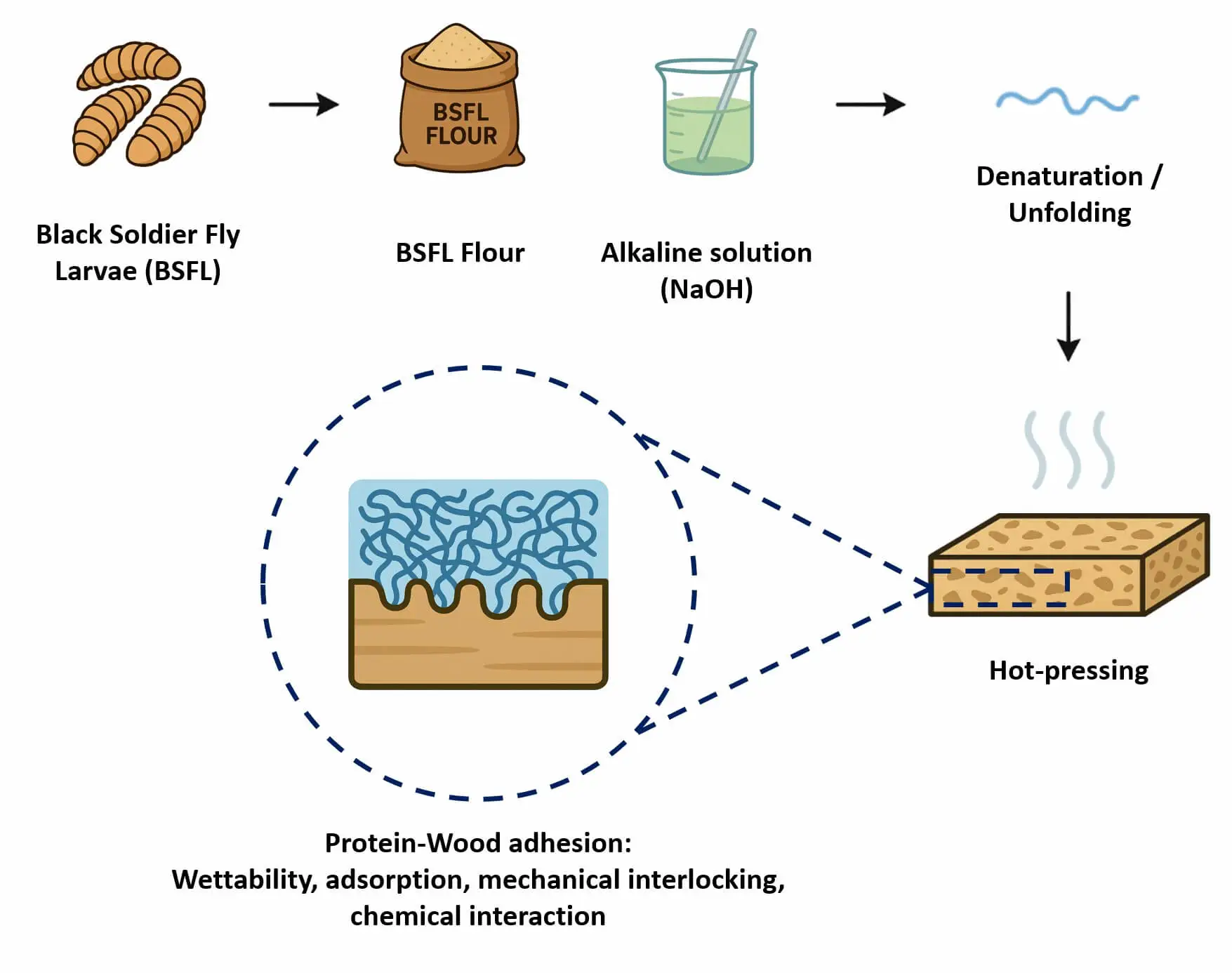
Abstract This study explores the use of black soldier fly larvae protein as a bio-based adhesive to produce particleboards from sugarcane bagasse. A comprehensive evaluation was conducted, including rheological characterization of the adhesive and physical–mechanical testing of the panels according to European standards. The black soldier fly larvae-based adhesive exhibited gel-like viscoelastic behavior, rapid partial structural recovery after shear, and favorable application properties. Particleboards manufactured with this adhesive and sugarcane bagasse achieved promising mechanical performance, with modulus of rupture and modulus of elasticity values of 30.2 and 3500 MPa, respectively. Internal bond strength exceeded 0.4 MPa,… More >
Graphic Abstract
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0146 - 23 January 2026
Abstract This study explores a novel method for processing cotton stalks—an abundant agricultural byproduct—into long strips that serve as sustainable raw material for engineered bio-based panels. To evaluate the effect of raw material morphology on panel’s performance, two types of cotton stalk-based panels were developed: one using long strips, maintaining fiber continuity, and the other using ground particles, representing conventional processing. A wood strand-based panel made from commercial southern yellow pine strands served as the control. All panels were bonded using phenol-formaldehyde resin and hot-pressed to a target thickness of 12.7 mm and density of 640 kg/m3.… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0157 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Process and Engineering of Lignocellulose Utilization)
Abstract Biomass is a resource whose organic carbon is formed from atmospheric carbon dioxide. It has numerous characteristics such as low carbon emissions, renewability, and environmental friendliness. The efficient utilization of biomass plays a significant role in promoting the development of clean energy, alleviating environmental pressures, and achieving carbon neutrality goals. Among the numerous processing technologies of biomass, hydrothermal carbonization (HTC) is a promising thermochemical process that can decompose and convert biomass into hydrochar under relatively mild conditions of approximately 180°C–300°C, thereby enabling its efficient resource utilization. In addition, HTC can directly process feedstocks with high… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0113 - 23 January 2026
Abstract This study aimed to produce and characterize mycelium leather (Mylea) derived from oil palm empty fruit bunch (OPEFB). Variations in OPEFB composition (10%, 20%, 30%, and 40%) were tested using a 10% w/w Ganoderma lucidum inoculum. The mycelium underwent boiling, plasticization, drying, pressing, waxing, and Tencel fabric reinforcement to form Mylea. The physical, mechanical, and flammability properties of OPEFB-based Mylea were evaluated as a potential animal leather substitute. The highest tensile strength (8.47 MPa) was observed in the 0% OPEFB sample due to reinforcement with the Tencel fabric layer. Meanwhile, the 20% OPEFB sample after drying More >
Graphic Abstract
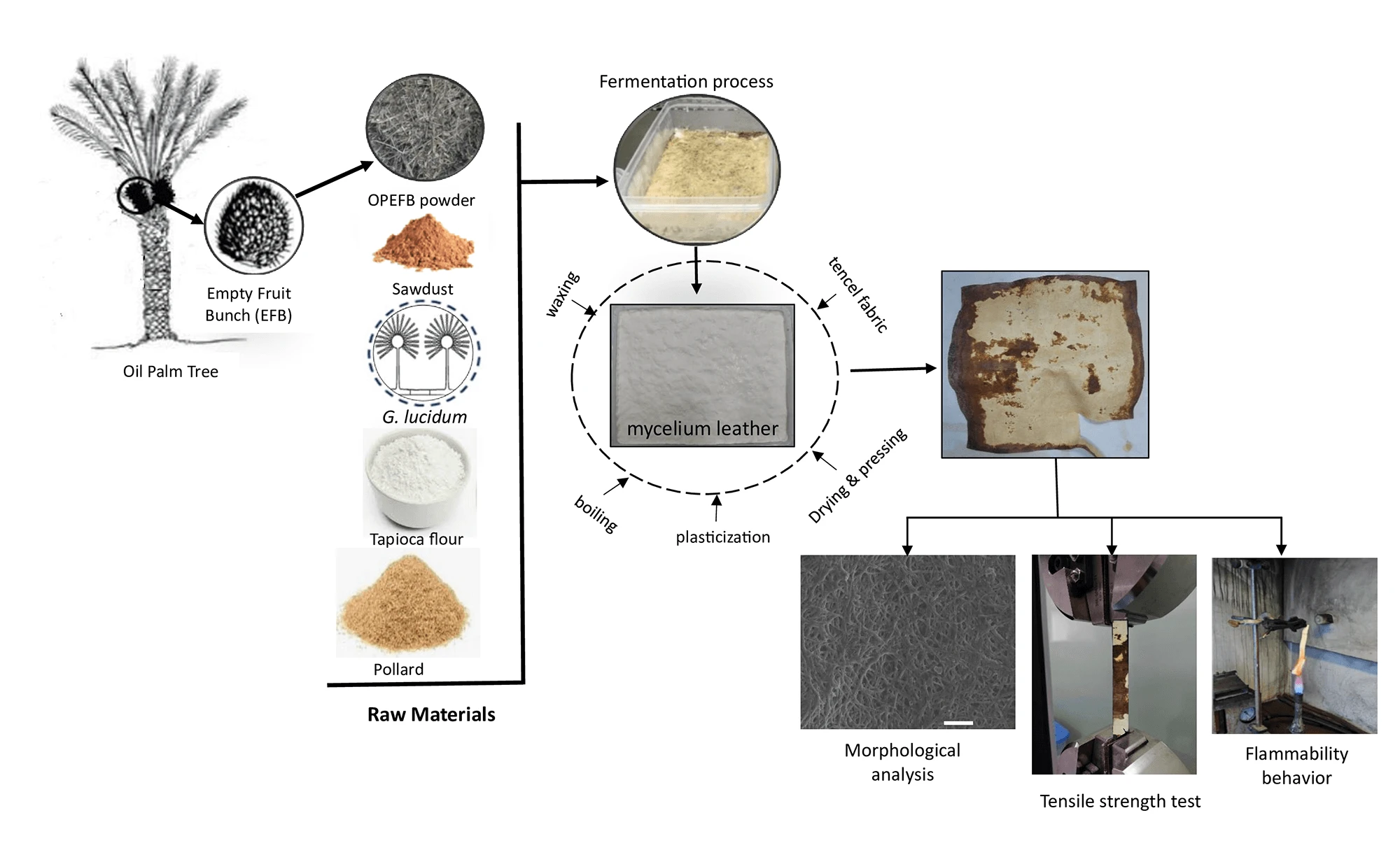
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0105 - 23 January 2026
Abstract In this study, Palm kernel shell (PKS) is utilized as a raw material to produce activated biochar as adsorbent for dye removal from wastewater, specifically methylene blue (MB) dye, by utilizing a simplified and cost-effective approach. Production of activated biochar was carried out using both a furnace and a domestic microwave oven without an inert atmosphere. Three samples of palm kernel shell (PKS) based activated biochar labeled as samples A, B and C were carbonized inside the furnace at 800°C for 1 h and then activated using the microwave-heating technique with varying heating times (0,… More >
 Open Access
Open Access
REVIEW
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0116 - 23 January 2026
(This article belongs to the Special Issue: Advances in Eco-friendly Wood-Based Composites: Design, Manufacturing, Properties and Applications – Ⅱ)
Abstract Typically used thermal insulation materials such as foam insulation and fibreglass may pose notable health risks and environmental impacts thereby resulting in respiratory irritation and waste disposal issues, respectively. While these materials are affordable and display good thermal insulation, their unsustainable traits pertaining to an intensive manufacturing process and poor disposability are major concerns. Alternative insulation materials with enhanced sustainable characteristics are therefore being explored, and one type of material which has gained notable attention owing to its low carbon footprint and low thermal conductivity is natural fibre. Among the few review studies conducted on… More >
Graphic Abstract
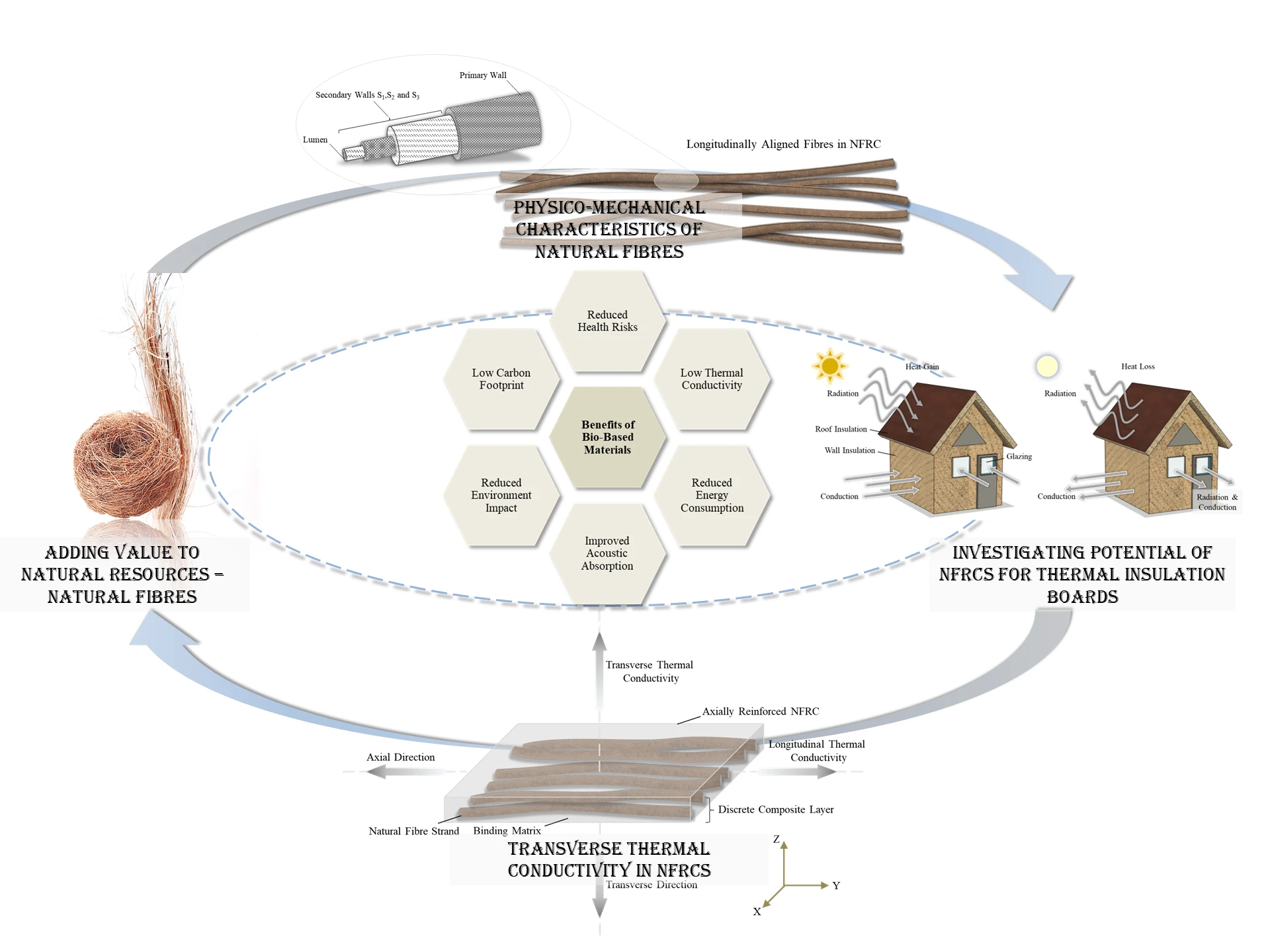
 Open Access
Open Access
ARTICLE
Journal of Renewable Materials, Vol.14, No.1, 2026, DOI:10.32604/jrm.2025.02025-0145 - 23 January 2026
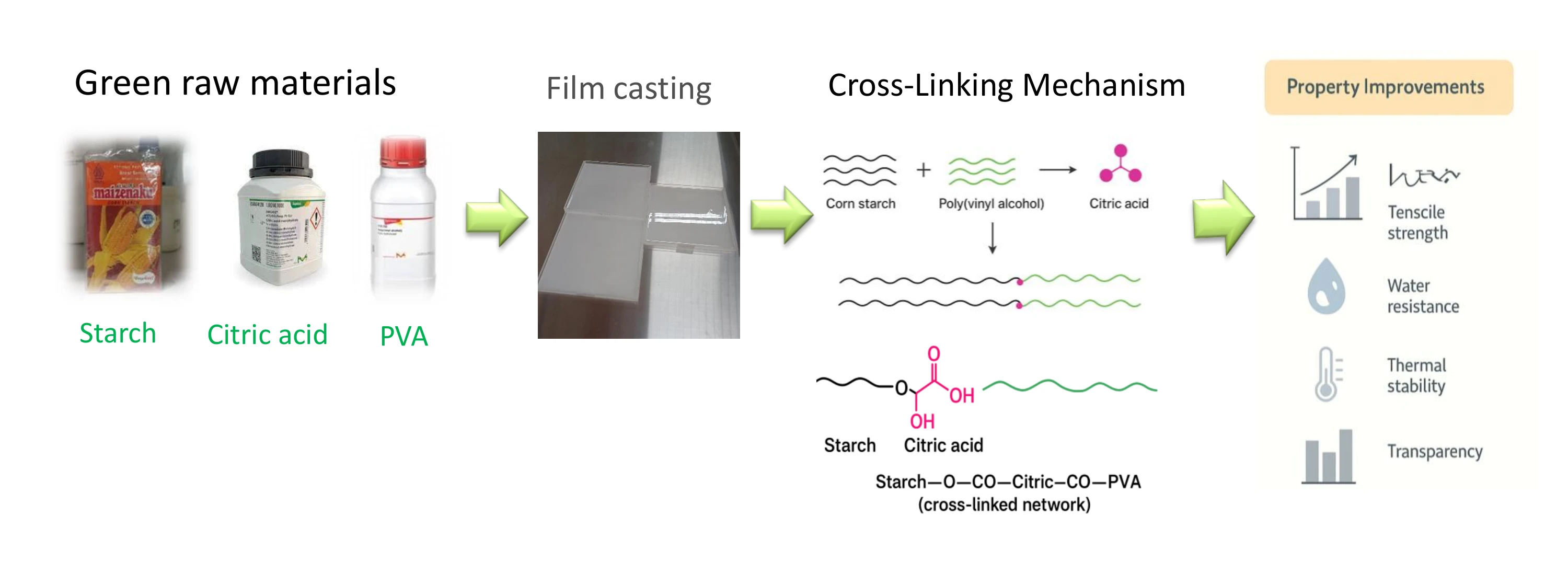
Abstract Corn starch (CS) is a renewable, biodegradable polysaccharide valued for its film-forming ability, yet native CS films exhibit low mechanical strength, high water sensitivity, and limited thermal stability. This study improves CS-based films by blending with poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) or glycerol (GLY) and using citric acid (CA) as a green, non-toxic cross-linker. Composite films were prepared by casting CS–PVA or CS–GLY with CA at 0%–0.20% (w/w of starch). The influence of CA on physicochemical, mechanical, optical, thermal, and water barrier properties was evaluated. CA crosslinking markedly enhanced the tensile strength, water resistance, and thermal stability More >
Graphic Abstract